Developing Video Games to Explore Exponentials and Logarithms in Culturally Relevant Scenarios
Video games offer an engaging entry point for students to explore the real-world applications of important mathematical concepts. During a Student Days minisymposium presentation at the 2024 SIAM Annual Meeting, which is taking place this week in Spokane, Wash., Ali Balooch of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas discussed the development of culturally relevant video games for Nevada college students in algebra and precalculus classes to aid active learning and strengthen conceptual understanding.
“The goal of this project is to help struggling math students, especially in algebra and geometry,” Balooch said. “We want to create engaging and interactive video games as well as Canvas applications.” The development team hopes that all students—regardless of background—will feel represented and included in the games, and places an emphasis on the regional needs of Nevada residents. Local instructors will be able to incorporate these video games into their classes as they best fit within the course structure.
The interdisciplinary project—which is funded by a National Science Foundation Hispanic-Serving Institution grant—includes Game Design and Canvas Design teams (both of which count Balooch as a member) as well as Education Outreach, External Evaluation, and Leadership teams. The project is split into five clusters that address different mathematical topics; Balooch’s presentation focused on the cluster that centers on exponential and logarithmic functions.
The Canvas application will be embedded within the online educational platform and explore various math-relevant scenarios; for instance, if an attendee at a concert sits a certain distance away from the stage, what volume of music will they hear? Answering this question requires students to make use of logarithms. Other problems will explore search algorithms (which are also relevant to logarithms) and radioactive decay (which deals in exponentials).
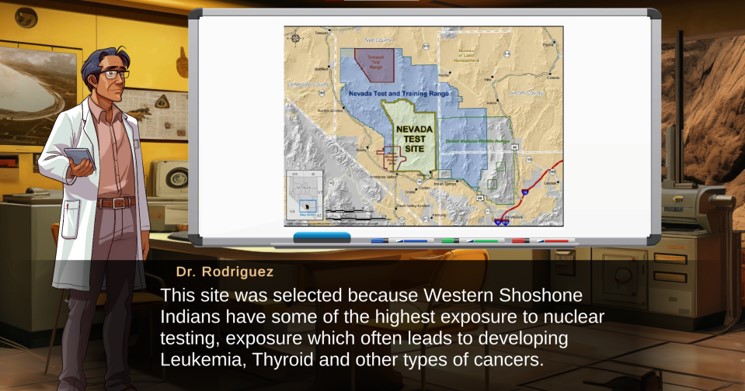
Balooch next described the current development stage of the video game, which is set in a fictional Nevada laboratory and includes four subgames. The first subgame explores exponential growth in the context of water treatment, based on an actual laboratory that tests the water quality of Lake Meade — a major water source in Nevada. The second subgame focuses on exponential decay through radioactivity, which also has a strong cultural relevance to the atomic testing that took place in Nevada during the 20th century (see Figure 1). Then, in the third subgames, students will use logarithms to investigate whether workers on the Las Vegas strip are exposed to unhealthily loud sound intensities (see Figure 2). “This showcases what inspires us to learn about these functions,” Balooch said.
The fourth subgame—which will unite the mathematical concepts from the prior three—is early in development, so Balooch presented several potential concepts. Perhaps this subgame could draw from the established genre of tower defense games, in which players must build defenses to impede enemies that are approaching on a predetermined path. To add cultural relevance to this gameplay, the theme could potentially be attempting to impede the movement of bacteria down a river before they reach the pipes that lead to household sinks. However, the fast-paced action inherent to this genre might make it hard for students to focus on the mathematics rather than pure strategy. Balooch also suggested that the subgame could feature species in the ocean who are competing to become the most powerful — though it was not yet determined how such a setup could incorporate logarithms.
Overall, the team is making good progress and is currently revamping graphics and revising content, as well as soliciting feedback from students and instructors. “We do hope that students find these games helpful and useful to learn about these topics,” Balooch said. And while interdisciplinary work does have its challenges and there was some initial friction between contributors from different subject areas, the collaboration is becoming a stronger and more cohesive unit. “I’m grateful to be a part of this team,” Balooch said. “It’s been really fun to work with everyone and see their viewpoints.”
Acknowledgements
This work is based on National Science Foundation Hispanic-Serving Institution grant #2225226. Ali Balooch acknowledged collaborators Raymond Ahn, Hayden Gomel, Annette Marin, Monika Neda, Daniel Sahl, Rachidi Salako, Blanca Rincon, and Vanessa Vongkulluksn of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas and Claudia Mora Bornholdt, John Howard, and Alok Pandey of the College of Southern Nevada.
About the Author
Jillian Kunze
Associate Editor, SIAM News
Jillian Kunze is the associate editor of SIAM News.



